Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
You can use the MongoDB Chatbot Server to perform retrieval augmented generation (RAG).
What is RAG?
RAG is a technique that improves chatbot response quality by grounding answers in a knowledge base. Before a user query is sent to an LLM to generate a response, the query is used to retrieve relevant information from a knowledge base. The LLM responds to the user query based on the information from the knowledge base.
By grounding the response in contextual information from the knowledge base, the chatbot can generate more relevant and accurate responses.
To learn more about RAG, refer to the article What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)? from MongoDB.
RAG Overview Diagram
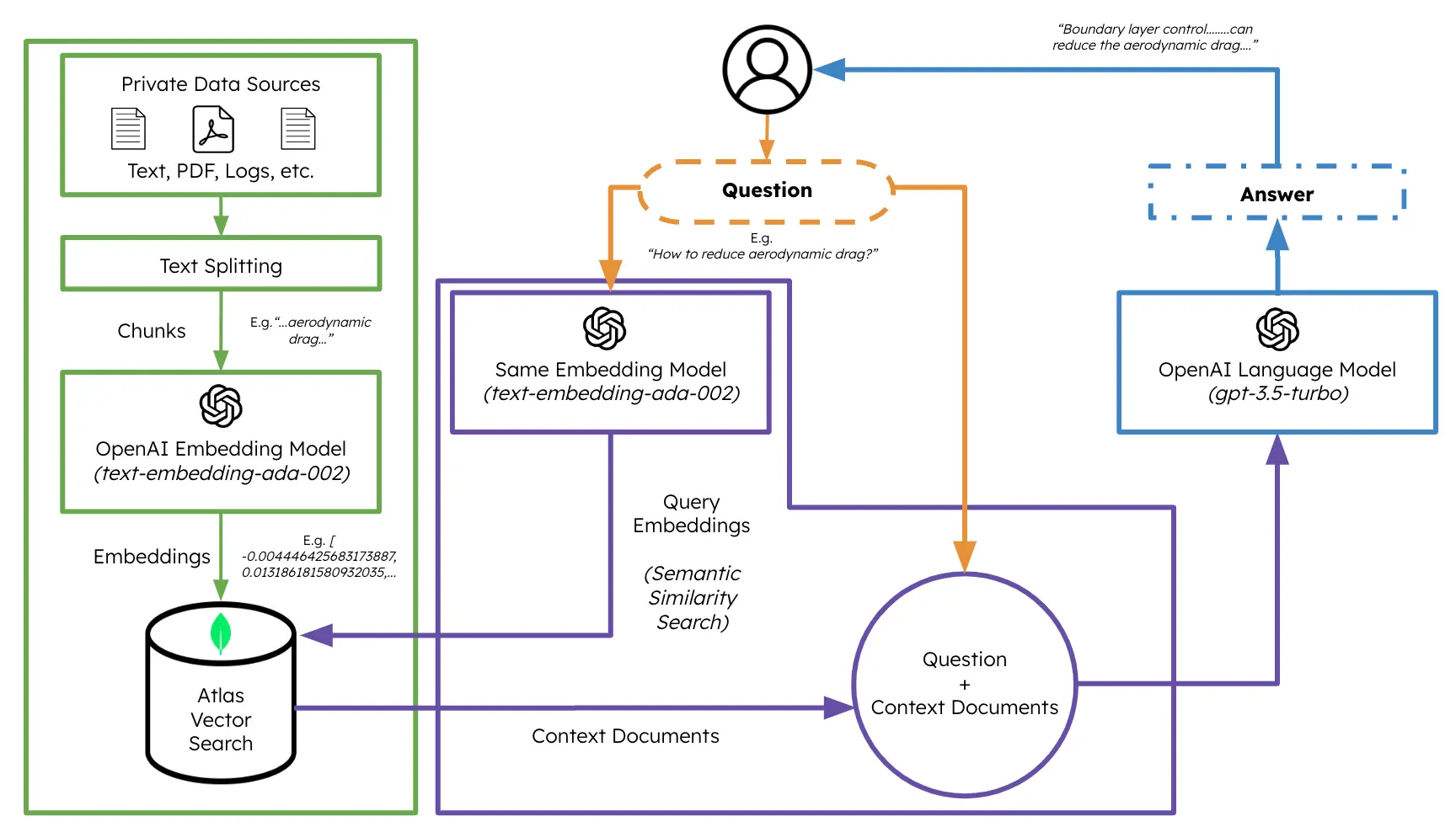
Generate User Message with RAG
You can perform RAG in the MongoDB Chatbot Server by implementing a GenerateUserPromptFunc function.
The MongoDB Chatbot Server comes with the makeRagGenerateUserPrompt() function that you can use to perform RAG with Atlas Vector Search.
Configure RAG
To configure the makeRagGenerateUserPrompt() function, include it in the
AppConfig.conversationsRoute.generateUserPrompt property.
import {
makeMongoDbEmbeddedContentStore,
makeOpenAiEmbedder,
makeMongoDbConversationsService,
AppConfig,
makeDefaultFindContent,
GenerateUserPromptFunc,
makeRagGenerateUserPrompt,
MakeUserMessageFunc,
} from "mongodb-chatbot-server";
import { stripIndents } from "common-tags";
import { makePreprocessMongoDbUserQuery } from "./processors/makePreprocessMongoDbUserQuery";
import { AzureOpenAI } from "mongodb-rag-core/openai";
// Make preprocessor
const mongoDbUserQueryPreprocessor = makePreprocessMongoDbUserQuery({
azureOpenAiServiceConfig: {
apiKey: OPENAI_API_KEY,
baseUrl: OPENAI_ENDPOINT,
deployment: OPENAI_CHAT_COMPLETION_DEPLOYMENT,
version: OPENAI_CHAT_COMPLETION_MODEL_VERSION,
},
numRetries: 0,
retryDelayMs: 5000,
});
export const embeddedContentStore = makeMongoDbEmbeddedContentStore({
connectionUri: MONGODB_CONNECTION_URI,
databaseName: MONGODB_DATABASE_NAME,
searchIndex: {
embeddingName: OPENAI_EMBEDDING_DEPLOYMENT,
}
});
export const embedder = makeOpenAiEmbedder({
openAiClient,
deployment: OPENAI_EMBEDDING_DEPLOYMENT,
backoffOptions: {
numOfAttempts: 3,
maxDelay: 5000,
},
});
export const findContent = makeDefaultFindContent({
embedder,
store: embeddedContentStore,
findNearestNeighborsOptions: {
k: 5,
path: "embedding",
indexName: VECTOR_SEARCH_INDEX_NAME,
minScore: 0.9,
},
});
// Make user message
export const makeUserMessage: MakeUserMessageFunc = async function ({
preprocessedUserMessage,
originalUserMessage,
content,
queryEmbedding,
}) {
const chunkSeparator = "~~~~~~";
const context = content.map((c) => c.text).join(`\n${chunkSeparator}\n`);
const contentForLlm = `Using the following information, answer the question.
Different pieces of information are separated by "${chunkSeparator}".
<Information>
${context}
<End information>
<Question>
${preprocessedUserMessage ?? originalUserMessage}
<End Question>`;
return {
role: "user",
content: originalUserMessage,
embedding: queryEmbedding,
preprocessedContent: preprocessedUserMessage,
contentForLlm,
};
};
export const generateUserPrompt: GenerateUserPromptFunc =
makeRagGenerateUserPrompt({
queryPreprocessor: mongoDbUserQueryPreprocessor,
findContent,
makeReferenceLinks: makeMongoDbReferences,
makeUserMessage,
});
export const config: AppConfig = {
conversationsRouterConfig: {
generateUserPrompt,
// ...
},
// ...
};
Data Flow
The makeRagGenerateUserPromptFunc() function has the following data flow:
- (Optional) Preprocess the user message. You can use this step to transform the user message before it is used to retrieve relevant content with to Atlas Vector Search. To learn more, refer to the Pre-process User Queries guide.
- Retrieve relevant content from Atlas Vector Search. To learn more, refer to the Retrieve Context Information guide.
- Removes any chunks that would exceed the max context tokens.
- Generate the user prompt and references based on the retrieved content.
- Return generated user prompt and references.
Also, you can reject the user message at any point in the flow. When the message is rejected, the server responds with a static response.